一、模拟散列表
例如我现在需要将$n(1\leq n \leq 10^5)$个数,每个数为$a_i(-10^9\leq a_i\leq 10^9)$进行映射,当然可以用unordered_map不过有些情况会被卡,所以这里手写哈希.
可能有人会说离散化,离散化是一种特殊的哈希,是需要保持哈希函数单调递增的.
将有一个函数为$h(x)\in (0,10^5)$,这个函数叫哈希函数.
一共有两种方法:
1.1 拉链法
拉链法:也就是对于$0$到$10^5-1$每次新加入的位置往下拉一条链,如图:
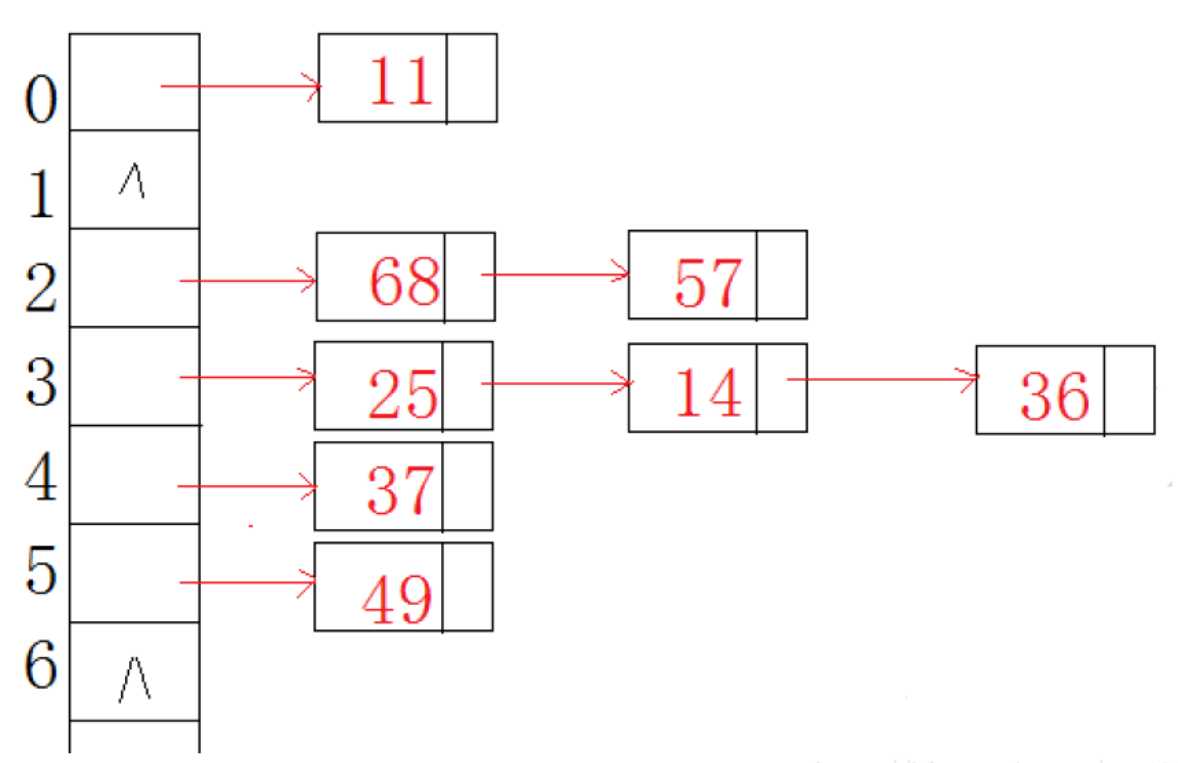
对于每一个就像拉链一样,与链式前向星很像
const int N = 100003;//质数
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
void insert(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;//模质数 因为负数模可能还是负数,得加
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = h[k];
h[k] = idx ++ ;
}//链式前向星
bool find(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
for (int i = h[k]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
if (e[i] == x)
return true;
return false;
}
...
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);//这样的 也可以写成0开始
if (find(x)) Yes;
else No;//举例 只需要用find函数即可
1.2 开放寻址法(重要)
注意映射要到$N$,我们的数组需要开到$2$到$3$倍。
每次找到一个位置h(x)=k,怎么找呢?类似于上厕所一样,这个坑位有人就往下,直到没有的地方。也是先取模加上再取模得到一个地方,如果有人则暴力加。
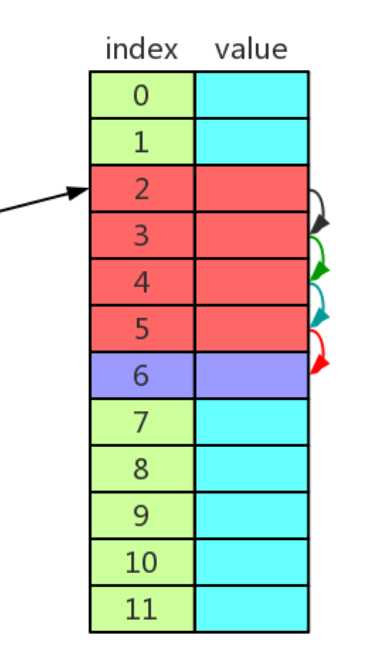
类似于上厕所一样,这个坑位有人就往下,直到没有的地方
const int N = 200003, null = 0x3f3f3f3f;//inf
int h[N];
int find(int x)
{
int t = (x % N + N) % N;
while (h[t] != null && h[t] != x)
{
t ++ ;
if (t == N) t = 0;
}
return t;
}
...
memset(h, 0x3f, sizeof h);
if (h[find(x)] == null) puts("No");
else puts("Yes");
二、字符串哈希
2.1 字符串哈希
这里的哈希函数包含着前缀和的思想,例如现在有一个字符串str="carrynotkarry",那么有如下值:
$h(0)=0$
$h(1)=c$
$h(2)=ca$
$h(3)=car$
这里的字母不是真的存入的是字符串,例如h(2)=ca并不是存的是"ca"而是存的ca的哈希值,例如ca的哈希值是226,那么这个h(2)=226,以后碰到值是226则表示是ca。
这里有个重要的思想就是把字符串看成p进制,例如:
$$
str=A\ B\ C\ D\ \Rightarrow \ (1\ 2\ 3\ 4)_p = 1\times p^3+2\times p^2+3\times p^1+4\times p^0
$$
但是这个数字可能很大,所以需要进行取模,对$Q$取模即可,所以得到的是$0$到$Q-1$的数字。
根据经验值来说,当P=131或者P=13331,然后Q=2^64的时候一般不会出错。(Q可以用unsigned long long自然溢出)
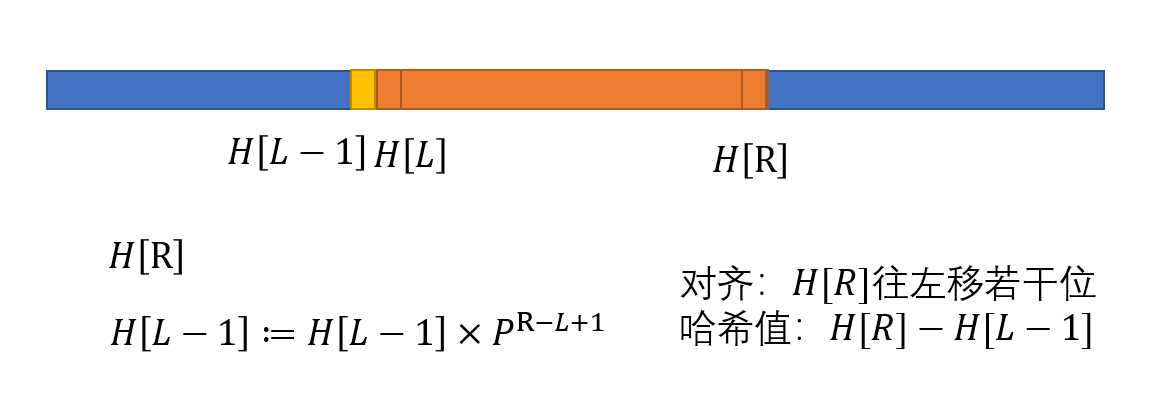
对齐和计算
板子题:给定一个长度为 $n$ 的字符串,再给定 $m$ 个询问,每个询问包含四个整数 $l_1,r_1,l_2,r_2$,请你判断 $[l_1,r_1]$ 和 $[l_2,r_2]$ 这两个区间所包含的字符串子串是否完全相同。
字符串中只包含大小写英文字母和数字。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const int N = 100010, P = 131;
int n, m;
char str[N];
ULL h[N], p[N];
ULL get(int l, int r)
{
return h[r] - h[l - 1] * p[r - l + 1];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
scanf("%s", str + 1);
p[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
h[i] = h[i - 1] * P + str[i];
p[i] = p[i - 1] * P;
}
while (m -- )
{
int l1, r1, l2, r2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &l1, &r1, &l2, &r2);
if (get(l1, r1) == get(l2, r2)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
return 0;
}
2.2 双哈希
两个值更加稳妥
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const int maxn = 600'000 + 5;
const ULL mod = 1000000007;
const ULL mod2 = 998244353;
const ULL base = 146;
ULL Sum1[maxn], Pow1[maxn];
ULL Sum2[maxn], Pow2[maxn];
map<pair<ULL,ULL>, int> P;
inline pair<ULL,ULL> get_hash(int l, int r){
ULL hash1 = (Sum1[r] - Sum1[l-1] * Pow1[r - l + 1] % mod + mod) % mod;
ULL hash2 = (Sum2[r] - Sum2[l-1] * Pow2[r - l + 1] % mod2 + mod2) % mod2;
return {hash1, hash2};
}
void init(char *s)
{
int n = strlen(s+1);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
Sum1[i] = (Sum1[i-1] * base % mod + s[i]) % mod;
Sum2[i] = (Sum2[i-1] * base % mod2 + s[i]) % mod2;
}
}
// code
Pow1[0] = Pow2[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 300000; i ++){
Pow1[i] = Pow1[i-1] * base % mod;
Pow2[i] = Pow2[i-1] * base % mod2;
}
pair<ULL,ULL> hashvalue = get_hash(l, r);
if (P.find(hashvalue) == P.end()) continue;
